
SchoolTutoring Academy is the premier educational services company for K-12 and college students. Interested in trigonometry tutoring services? Learn more about how we are assisting thousands of students each academic year. only 200 years to travel the angular diameter of the moon across the sky. Observations from the Hubble Space Telescope can detect distances to stars over 10,000 light years away. The parallax can be used to measure the distance to the few stars which are. Its companion Gaia mission measured the distances to over a billion stars.

The Hipparcos satellite was launched in 1989, specifically to measure parallax to distant stars, up to about 1600 light-years away. The most accurate measurements of parallax are being made far from the obscuring atmosphere of earth. Usable measurements of parallax weren’t possible until the middle of the 19 th century. It is equal to about 3.26 light years, an unimaginable distance to astronomers in the 1600s and 1700s.
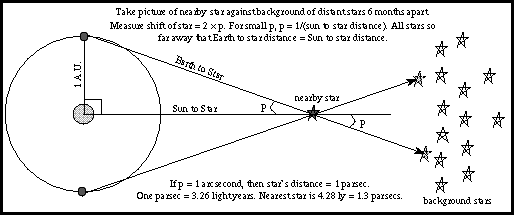
The parsec is a unit of measure that is based upon parallax. By accurately measuring the defect because of parallax. The measurement of the parallax of stars outside the solar system uses such small angles that ancient astronomers could not measure them precisely enough. RT nonayousef7: ( 22 / 05 / 2018 ) Throwback Repost from itsSSR Parallax is the way an object’s position or direction seems to change depending on viewing angle. Then, similar calculations can be done to estimate the distance to the other celestial object. For example, apparent motion can be measured in January and in June. The principle of measuring solar parallax, or parallax to any of the other planets or asteroids in the solar system, uses a baseline measurement of the earth at opposite locations of its orbit. According to the principles of trigonometry, if the baseline of the triangle is known, as well as the top angle (measured in fractions of arcseconds), the length of the long side can be estimated accurately. This varies with the altitude of the Moon. If O is the observer on the surface of Earth, E the centre of Earth, and M the position of the Moon, then the angle OME is the parallax. The moon is the closest celestial object to the earth, so the angle that can be estimated from its movement is the largest, at nearly one degree. The parallax of the Sun or Moon is defined as the difference in direction as seen from the observer and from Earth’s centre. The apparent position of the moon in the sky will be at a different angle as seen from one observatory than from another at a different location. Imagine a circle around the earth with 2 observatories roughly at opposite sides of the earth from each other, such as Calgary, Canada and Pretoria, South Africa. The principles of triangulation are used to measure distances for all celestial objects. Astronomers use the very small angles observed by parallax to estimate distances and relative motion of objects ranging from the sun, moon, and planets to distant stars. It is the measurement of how the same object appears from two different points of view. That means it can measure, to within 20 percent accuracy, the distances of stars that lie tens of thousands of light-years away.The demonstration of parallax is as close as an observer’s own two eyes. The European Space Agency’s Gaia mission, currently underway, can measure parallax angles of just a few millionths of an arcsecond. That’s why a parsec has that value, and not any other.Īlthough astronomers often measure distant objects in parsecs or megaparsecs (1 megaparsec is 1 million parsecs), only nearby objects have parallaxes that we can actually measure. And a parsec is the distance - 3.26 light-years - that a star must lie from the Sun for its parallax angle to be exactly 1″. The two different sightlines, one at each end of Earth’s orbit, create a triangle the parallax angle is defined as half the angle at the triangle’s apex. If you draw a simple diagram, you’ll see that the distance the star appears to move is related to the angle at which it is viewed. Translated to the stars in the sky, two photographs of the same nearby star taken six months apart will show it appearing to move against the background of more distant stars because Earth has moved to the other side of the Sun in its orbit. Your finger will appear to shift because each eye views it from a slightly different angle. Next, open your left eye and close your right. Close just your left eye and observe where your finger appears against the background. One of the simplest ways to see for yourself how this works is to hold your hand at arm’s length in front of your face and raise one finger. This is because as our planet moves, our viewpoint changes. Over the course of several months, nearby stars appear to move with respect to more distant objects - an effect called parallax. Earth circles the Sun, making one complete orbit per year. Question: Why is a parsec 3.26 light-years and not some other number?Īnswer: A parsec, or “parallax second,” is defined as 3.26 light-years because of how it is measured.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
